The Tag Life Cycle with Attributes in JSP
By: Fazal in JSP Tutorials on 2007-10-06
Introducing attributes into a custom tag does change the tag life cycle slightly because before the functionality of the tag can be executed (the doTag() method in the case of simple tags), the attributes must be passed to the tag handler so that they can be used by the tag. The way that the JSP specification allows this is through properties and setter methods of the tag handler class. A tag handler must have a property and a setter method for every attribute that it supports.
Note The necessity for the tag handler to have a property and setter method for every supported attribute is a requirement of previous versions of the JSP specification. But with the introduction of dynamic attributes, this is not strictly true anymore.
These setter methods must conform to the standard JavaBeans naming convention, meaning that to support an attribute called name of type String, the tag handler must declare a setter method with the following signature:
public void setName(String s)
In this example, at request time, the value of the name attribute will be passed to the setName() method. With this in mind, you can now see how supporting attributes alters the tag life cycle. As an example, consider the following custom tag usage:
<prefix:myTag attribute1="abc" attributeN="def"/>
Here, the tag has two attributes that are being specified. By looking at the tag life cycle in Figure below, you can see what happens behind the scenes.\
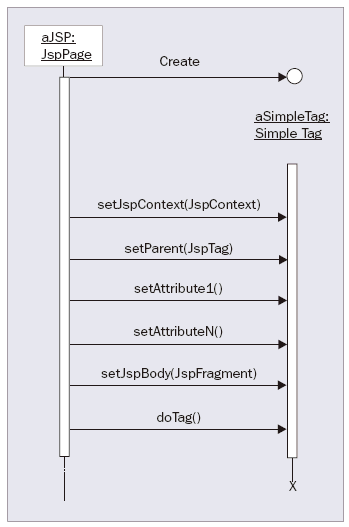
The life cycle of a simple tag with parameters
As this diagram shows, the setter methods for the attributes are called before the doTag() method is executed, and in the same order that the attributes appear within the usage of the tag, from left to right. When it comes to implementing attributes in tag handler classes, attribute setter methods typically store a copy of the attribute away in an instance variable, ready for the doTag() method to use.
Add Comment
This policy contains information about your privacy. By posting, you are declaring that you understand this policy:
- Your name, rating, website address, town, country, state and comment will be publicly displayed if entered.
- Aside from the data entered into these form fields, other stored data about your comment will include:
- Your IP address (not displayed)
- The time/date of your submission (displayed)
- Your email address will not be shared. It is collected for only two reasons:
- Administrative purposes, should a need to contact you arise.
- To inform you of new comments, should you subscribe to receive notifications.
- A cookie may be set on your computer. This is used to remember your inputs. It will expire by itself.
This policy is subject to change at any time and without notice.
These terms and conditions contain rules about posting comments. By submitting a comment, you are declaring that you agree with these rules:
- Although the administrator will attempt to moderate comments, it is impossible for every comment to have been moderated at any given time.
- You acknowledge that all comments express the views and opinions of the original author and not those of the administrator.
- You agree not to post any material which is knowingly false, obscene, hateful, threatening, harassing or invasive of a person's privacy.
- The administrator has the right to edit, move or remove any comment for any reason and without notice.
Failure to comply with these rules may result in being banned from submitting further comments.
These terms and conditions are subject to change at any time and without notice.
- Data Science
- Android
- React Native
- AJAX
- ASP.net
- C
- C++
- C#
- Cocoa
- Cloud Computing
- HTML5
- Java
- Javascript
- JSF
- JSP
- J2ME
- Java Beans
- EJB
- JDBC
- Linux
- Mac OS X
- iPhone
- MySQL
- Office 365
- Perl
- PHP
- Python
- Ruby
- VB.net
- Hibernate
- Struts
- SAP
- Trends
- Tech Reviews
- WebServices
- XML
- Certification
- Interview
Comments