MVC Architecture (Model 2 Architecture)
By: Baski in Struts Tutorials on 2007-09-13
The Model 2 architecture for designing JSP pages is in reality, Model View Controller
(MVC) applied to web applications. Hence the two terms can be used interchangeably in the web world. MVC originated in SmallTalk and has since
made its way into Java community. Model 2 architecure and its derivatives are the cornerstones for all serious and industrial strength web applications designed
in the real world. Hence it is essential for you understand this paradigm thoroughly. Figure 1.2 shows the Model 2 (MVC) architecture.
The main difference between Model 1 and Model 2 is that in Model 2, a controller handles the user request instead of another JSP. The controller is
implemented as a Servlet. The following steps are executed when the user submits the request.
- The Controller Servlet handles the user's request. (This means the hyperlink in the JSP should point to the controller servlet).
- The Controller Servlet then instantiates appropriate JavaBeans based on the request parameters (and optionally also based on session attributes).
- The Controller Servlet then by itself or through a controller helper communicates with the middle tier or directly to the database to fetch the required data.
- The Controller sets the resultant JavaBeans (either same or a new one) in one of the following contexts - request, session or application.
- The controller then dispatches the request to the next view based on the request URL.
- The View uses the resultant JavaBeans from Step 4 to display data. Note that there is no presentation logic in the JSP. The sole function of the
JSP in Model 2 architecture is to display the data from the JavaBeans set in the
request, session or application scopes.
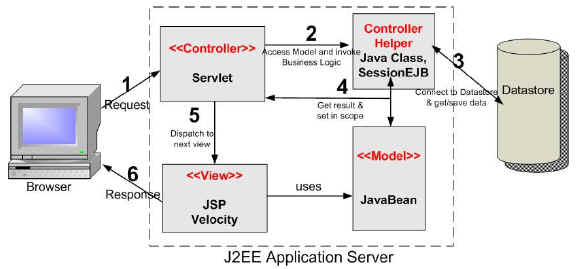
Model 2 Architecture.
Advantages of Model 2 Architecture
Since there is no presentation logic in JSP, there are no scriptlets. This means
lesser nightmares. [Note that although Model 2 is directed towards elimination of
scriptlets, it does not architecturally prevent you from adding scriptlets. This has
led to widespread misuse of Model 2 architecture.]
With MVC you can have as many controller servlets in your web application. In fact you can have one Controller Servlet per module. However there are
several advantages of having a single controller servlet for the entire web application. In a typical web application, there are several tasks that you want to
do for every incoming request. For instance, you have to check if the user requesting an operation is authorized to do so. You also want to log the user"s
entry and exit from the web application for every request. You might like to centralize the logic for dispatching requests to other views. The list goes on. If
you have several controller servlets, chances are that you have to duplicate the
logic for all the above tasks in all those places. A single controller servlet for the
web application lets you centralize all the tasks in a single place. Elegant code
and easier to maintain.
Web applications based on Model 2 architecture are easier to maintain and extend since the views do not refer to each other and there is no presentation
logic in the views. It also allows you to clearly define the roles and responsibilities in large projects thus allowing better coordination among team
members.
Add Comment
This policy contains information about your privacy. By posting, you are declaring that you understand this policy:
- Your name, rating, website address, town, country, state and comment will be publicly displayed if entered.
- Aside from the data entered into these form fields, other stored data about your comment will include:
- Your IP address (not displayed)
- The time/date of your submission (displayed)
- Your email address will not be shared. It is collected for only two reasons:
- Administrative purposes, should a need to contact you arise.
- To inform you of new comments, should you subscribe to receive notifications.
- A cookie may be set on your computer. This is used to remember your inputs. It will expire by itself.
This policy is subject to change at any time and without notice.
These terms and conditions contain rules about posting comments. By submitting a comment, you are declaring that you agree with these rules:
- Although the administrator will attempt to moderate comments, it is impossible for every comment to have been moderated at any given time.
- You acknowledge that all comments express the views and opinions of the original author and not those of the administrator.
- You agree not to post any material which is knowingly false, obscene, hateful, threatening, harassing or invasive of a person's privacy.
- The administrator has the right to edit, move or remove any comment for any reason and without notice.
Failure to comply with these rules may result in being banned from submitting further comments.
These terms and conditions are subject to change at any time and without notice.
- Data Science
- Android
- React Native
- AJAX
- ASP.net
- C
- C++
- C#
- Cocoa
- Cloud Computing
- HTML5
- Java
- Javascript
- JSF
- JSP
- J2ME
- Java Beans
- EJB
- JDBC
- Linux
- Mac OS X
- iPhone
- MySQL
- Office 365
- Perl
- PHP
- Python
- Ruby
- VB.net
- Hibernate
- Struts
- SAP
- Trends
- Tech Reviews
- WebServices
- XML
- Certification
- Interview
categories
Related Tutorials
Handling Duplicate Form Submissions in Struts
Guidelines for Struts Application Development
Configuring JDBC DataSources in Struts
When is the best time to validate input in Struts
Simple example of using the requiredif Validator rule in Struts
How to prepopulate a form in Struts
Using JavaScript to submit a form in Struts
FAQ: Why are my checkboxes not being set from ON to OFF?
FAQ: Why was reload removed from Struts (since 1.1)?
Comments